Music-Induced Goosebumps Linked to Special Brain Structure, Study Finds
Getting goosebumps from music is a unique physiological response that only certain people can experience, according to scientific research. This phenomenon is linked to special neural connections in the brain.
A study by Harvard researcher Matthew Sachs revealed that people who get music-induced goosebumps have a denser volume of fibers connecting their auditory cortex to emotional processing areas. This distinct brain structure allows for stronger emotional responses to musical stimuli.

Goosebumps with water droplets on skin
The sensation often includes:
- Shivers down the spine
- Goosebumps on the skin
- Altered breathing patterns
- Slowed heart rate
- Heightened awareness of the music
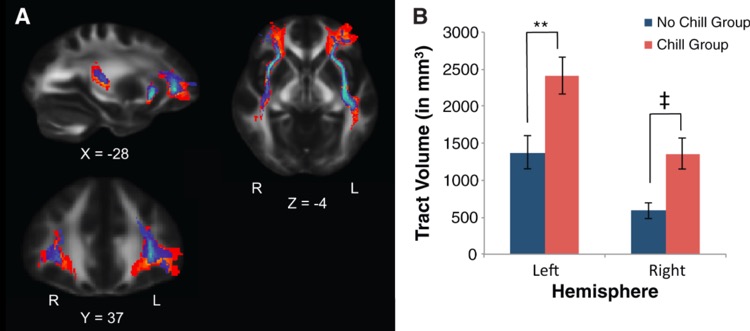
Brain scan showing music-induced goosebumps
While the exact percentage of people who experience this phenomenon is still unknown, the initial study examined 20 participants carefully selected from a group of 237. Half reported experiencing music-induced goosebumps, while the other half did not.
Interestingly, some individuals cannot experience pleasure from music at all, despite normal responses to other rewards like money. This research could have significant implications for treating depression, as music's ability to trigger intense pleasure responses could be valuable in therapeutic settings.
The findings provide the first scientific evidence for neural differences in how individuals process and respond emotionally to music, suggesting that music's role in social-emotional communication may have evolutionary significance in human development.